Why Is It Important To Monitor Your Children's Oral Habits?
An essential aspect of the overall health of children is their oral hygiene. Their oral habits must be monitored and taken care of as soon as they get their first tooth! Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit, pediatric dentist from Pandit’s Clinic, Pune, informs us that this can be as early as 6 to 9 months of age and is even applicable for newborns with neonatal teeth (teeth present at the time of birth).
Dr. Pratibha says that as children are too small to understand the importance of dental health, it is imperative for parents or caretakers to monitor their child’s oral hygiene and to keep a watch on any faulty habits which may sabotage their dental and oral development. Sometimes a seemingly harmless habit can cause severe dental or oral issues later in life.
3 Oral Habits To Watch Out For
Listed here are three commonly seen bad habits seen in children and how you can break them:
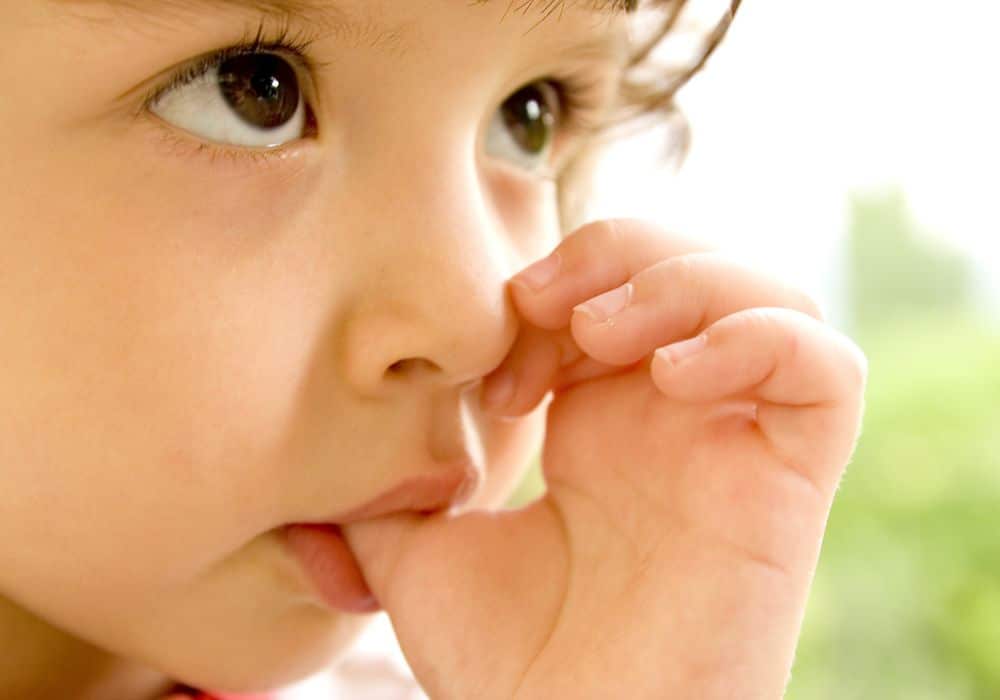
Thumbsucking
Causes of thumbsucking
Thumbsucking usually develops as a later phase of fingersucking, which is a common thing to do for infants as they are developing their cognitive abilities. Fingersucking in the early stages of infancy is beneficial to help build a brain-sensory response to help them understand feeding and eating.
Some kids also develop the habit of thumbsucking to soothe themselves or to feel comfortable. Usually, it is a harmless habit, but thumbsucking which continues beyond the age of the eruption of permanent teeth can cause severe oral issues and extensive orthodontic treatment later in life.
Thumbsucking also develops as a replacement for children who indulge in pacifier use for a long time, especially after the age of two.
Effects of thumbsucking
- Difficulty in eating
- Difficulty in speaking and forming words
- Maxilla(upper jaw) deformation
- Deep palate
- Proclined incisors
- Open bite
- Generalized malalignment of teeth
- Incompetent lips(lips that don't close completely)
Ways to break the habit
It is generally observed that children quit thumbsucking after reaching a certain age. However, pediatric dentist Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit warns that there might be instances when a child is not in favor of quitting the habit. Therefore, parents should consider a few things while taking steps to break this habit in young children.
Parents may need to practice positive reinforcement and rewards for children who do not indulge in thumbsucking. Negative reinforcement, like scolding and nagging, may have a detrimental impact. It may cause the child to practice the habit even more out of fear or anxiety.
In older children, parents should try to find out and counsel the reason why children are not quitting sucking their thumbs or fingers. Professional counseling can help quit thumbsucking. Efforts should be made to understand and eliminate the cause of the action.
If all these steps do not help, a dentist can help to fit orthodontic appliances in the upper front teeth, which fit snugly against the palate. This appliance helps to make thumbsucking more difficult and unpleasant.
Mouth Breathing
Causes of mouth breathing
- You can be sure that your child is mouth breathing when you notice your child snoring. Snoring happens in anatomical discrepancies like enlarged adenoids or tonsil obstruction. Sleep apnea (difficulty breathing when sleeping) due to these reasons causes the child to start mouth breathing.
- Mucus secretion from the sinuses or sinus block can cause difficulty sleeping. The child then starts mouth breathing.
- Anatomical problems like a deviated nasal septum can cause the narrowing of the nasal passages, making breathing difficult. This leads to mouth breathing.
- When a child stops breastfeeding before three months of age, he/she is more at risk of developing mouth breathing. Prolonged use of pacifiers is also associated with mouth breathing.
- Tongue tie causes improper growth of pro-facial muscles causing the mouth to remain open or nasal passages to be blocked. This leads to mouth breathing.
- Continuous drainage and sinus allergies cause breathing difficulties. This can cause mouth breathing.
Effects of mouth breathing
- Inhaled air is not cleared of toxins
- Dry mouth that causes gingival infections and tooth decay
- Oro-facial malocclusion
- Speech problems due to the thrusting action of the tongue (lisping)
- Sleep apnea or snoring
Ways to break the habit
- Breastfeeding at least once a day to help oral tone muscles for small infants until one year of age
- Getting rid of pacifiers at the appropriate time
- Treatment of allergies
- Treatment of tongue ties, adenoids, tonsils, or deviated nasal septum
- A dentist can help with fitting an orofacial appliance to help guide jaw movement
Lip And Nail Biting
Many children tend to bite their lips or their nails. Pediatric dentist Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit explains that it is mostly a habit that ceases as a child grows, but sometimes intervention may be required to stop lip and nail biting.
Causes of lip and nail biting
- When children are not engaged enough in any activity and have extra time doing nothing, they tend to chew their lips or nails to pass the time.
- Some children are not very good at handling stressful, anxious situations, which triggers lip or nail biting.
- Some children also find that nail biting helps to get calm or to fall asleep.
Effects of lip and nail biting
- Jaw pain
- Unsightly nails
- Transfers infections from nails to mouth
- Nail infections due to oral bacteria
- Teeth cavities
- Microfractures in tooth structure
Ways to break the habit
- Counseling to break the habit
- Cut and keep the nails short always
- Get them clay, play putty, and fidget toys to keep their hands occupied
- Applying bitter nail polish to avoid nail biting
When should you see a Pediatric Dentist?
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit, pediatric dentist from Pandit’s Clinic, Pune, says that most oral habits are usually just a passing phase. Therefore, you usually do not need to worry about them. Still, if you notice that your child has any of these habits for a prolonged period and is not showing any signs of giving it up, then it is essential to talk to a pediatric dentist as soon as possible. A pediatric dentist can provide personalized advice and treatment for your child’s oral health needs.
Why Are Regular Dental Visits Important?
If you have any questions or concerns, please don’t hesitate to contact us at +918805980048 / +91-7888229284 or book an appointment with Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit.
Virtual Video Consultations
100% SAFE AND SECURE CALLS WITH ENCRYPTION. YOUR PRIVACY AND CONFIDENTIALITY IS GUARANTEED.
Start here, by making an appointment for a virtual consultation with our expert Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit (NEW PATIENTS ONLY).
Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit is available for Virtual Video Consultations from Monday – Saturday between the hours of 11 am – 2pm and 4pm – 7pm.
If you are already our valued patient with questions or have an emergency please contact the clinic on +91 9822053446
Consult Dr. Pratibha Kukreja Pandit
(Pediatric Dentist)
Virtual Video Consultation Fees Rs. 500
The Consultation Fees Must Be Paid Online by GOOGLE PAY BEFORE YOUR APPOINTMENT. See The Instructions On Appointment Confirmations
Your virtual video consultation includes:
- Discussion of problems that your child is facing like tooth pain, swelling or any other emergencies
- Dr. Pratibha will recommend a course of treatment or medications for your child.
Meet the Doctor
Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry Specialist
Dr. Pratibha is the Chief Dentist at Pandit Clinic. She is also a Consultant Pediatric Dentist at Kotbagi Hospital and KEM Hospital, Pune.
Dr. Pratibha has trained at the prestigious Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan, in advanced areas including Pediatric dental treatment under General Anesthesia and Intravenous sedation, Dental Rehabilitation of children with special health care needs, and Nasoalveolar molding and dental rehabilitation of cleft lip and cleft palate.
She’s the lifetime member of Student Clinician Association, American Dental Association (SCADA), USA.
Professional Affiliations and Skills
- Trained in Pediatric dental treatment under General Anesthesia and Intravenous sedation at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan
- Trained in Dental Rehabilitation of children with special health care needs at CGMH, Taiwan
- Trained in Nasoalveolar molding and dental rehabilitation of Cleft lip and Cleft Palate at craniofacial centre, CGMH, Taiwan
- Awarded Lifetime membership, SCADA (Student Clinician Association, American Dental Association), USA.
You Might Be Interested In

The Importance of Space Maintainers For Children’s Teeth
Primary or milk teeth are responsible for many essential functions of our young ones, like chewing, smiling, talking, and maintaining space in the jaws for
How Fluoride Can Prevent Cavities In Kids
Fluoride is a naturally found mineral that plays an important role in keeping the teeth enamel safe and preventing cavities. Children with fluoride deficiency are